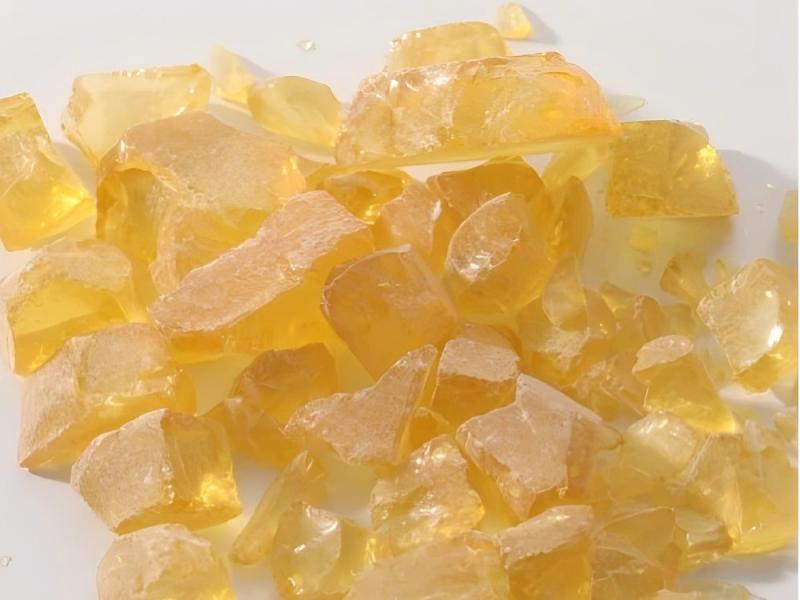
Fumaric acid is derived from both natural and synthetic sources. This compound is widely distributed. It can be found in fruits and vegetables such as apples, grapes, berries, tomatoes, and carrots. Fungi such as ‘Rhizopus’, ‘Aspergillus’, and ‘Penicillium’ can also produce fumaric acid in soil. In the human body, fumaric acid helps in energy production. Factories use fermentation and chemical methods to produce fumaric acid to meet growing demand.
Key Takeaways
- Fumaric Acid for foods and beverages, such as apples, grapes, and tomatoes. This makes it easy to add to one’s daily diet.
- This compound is essential for energy production in the human body and helps cells function properly.
- Fumaric acid is produced in factories using fermentation. This method is environmentally friendly and allows for long-term storage.
- Fumaric acid is added to food to improve taste and maintain freshness. This helps make food safer and more delicious.
- In the medical field, fumaric acid helps treat diseases such as psoriasis. This shows that its importance extends beyond food and manufacturing.
Natural Sources of Fumaric Acid

Plants and Fungi
Fumaric acid is found in many plants and fungi. Some plants, such as Arabidopsis thaliana and soybeans, are rich in fumaric acid. Arabidopsis leaves can contain several milligrams of fumaric acid per gram. Sometimes, their fumaric acid content even exceeds that of starch or sugars. This makes these plants very useful to scientists and businesses.
Wild plants can also produce fumaric acid. Corydalis, Iceland moss, and lichens are natural sources. Boletus and button mushrooms are rich in fumaric acid. Button mushrooms have a higher fumaric acid content than other organic acids, which gives them their unique flavor. Iceland moss and lichens grow in harsh environments and are beneficial to the environment.
Fungi play an important role in the natural synthesis of fumaric acid. Rhizopus oryzae, Rhizopus arrhizus, and Rhizopus delemar can all synthesize large amounts of fumaric acid. Their synthesis efficiency is highest when nitrogen content is low. These fungi utilize the reducing tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) to efficiently synthesize fumaric acid. The table below lists the fumaric acid synthesis rates of different fungi:
| Fungal Species | Typical Yield (g/L) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Rhizopus oryzae | Up to 32.1 | Highest yield; commonly used in industrial production |
| Rhizopus arrhizus | 6–8.4 | Good yield; requires a special carrier |
| Rhizopus delemar | Similar to R. oryzae | Sometimes considered same as R. oryzae |
| Aspergillus niger | 0.7 | Yield lower than ‘Rhizopus’ fungi |
| Aspergillus terreus | 0.8 | Utilizes wheat bran; yield increases over time |
| Aspergillus oryzae | 0.6 | Lower yield; growth plateaus after 120 hours |
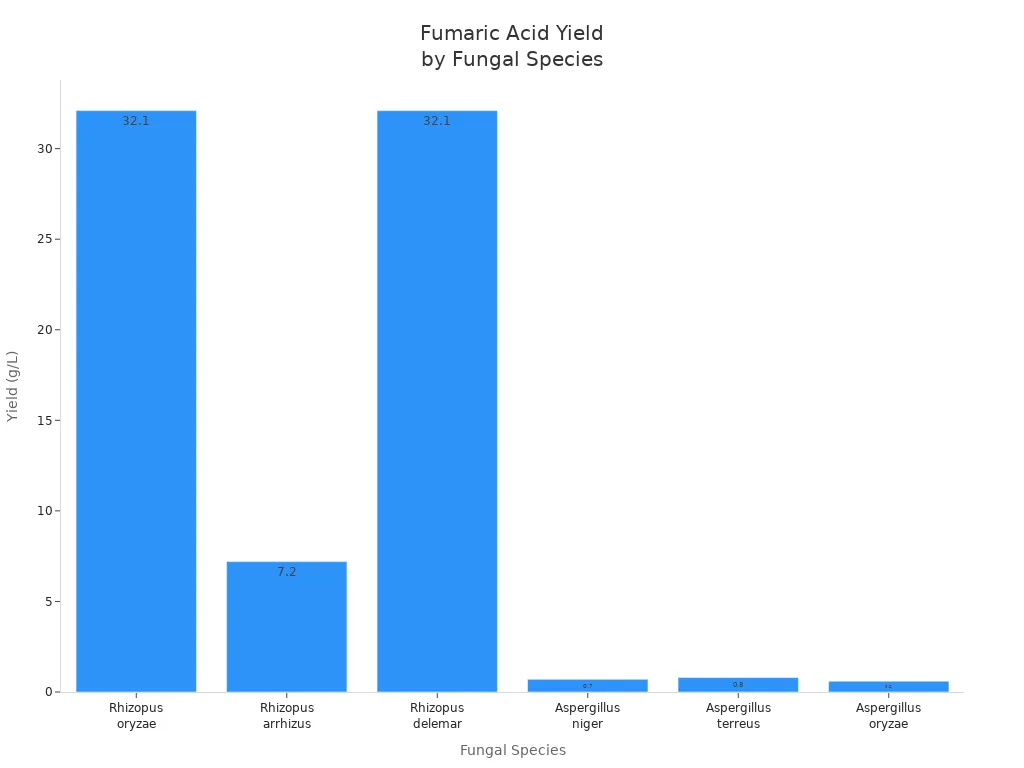
Rhizopus oryzae produces the most fumaric acid. Therefore, it is commonly used in large-scale production in factories.
Note: The fumaric acid content in plants and fungi can vary. This depends on their growing location, weather, and other conditions. For example, the fumaric acid content of blueberries may differ between years and regions.
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are also sources of fumaric acid. Many foods we eat contain this compound. This means that people frequently obtain fumaric acid from their diet. Here are some foods rich in fumaric acid:
- Apples
- Grapes
- Berry
- Tomatoes
- Carrots
These foods taste delicious and provide the body with important organic acids. The table below shows that apples, tomatoes, and carrots contain fumaric acid:
| Fruit/Vegetable | Fumaric Acid Presence |
|---|---|
| Apples | Confirmed |
| Tomatoes | Confirmed |
| Carrots | Confirmed |
The fumaric acid content in these foods can vary. Soil, weather, and year all affect its content. Blueberries may have a higher fumaric acid content in some years. The fumaric acid content in wild strawberries typically remains constant.
Fumaric acid imparts a sour taste to fruits and vegetables, adding to the appealing flavor of fresh foods. Consuming these foods provides the body with naturally occurring fumaric acid.
Fumaric Acid Metabolism in the Body
Human Metabolic Pathways
The metabolism of fumaric acid occurs within cells. The body utilizes the Krebs cycle to generate energy. This cycle takes place in the mitochondria, known as the cell’s “powerhouse.” The following steps illustrate the formation of fumaric acid:
- Pyruvate originates from the breakdown of sugars and enters the Krebs cycle.
- Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA.
- Acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate.
- Citrate is converted to isocitrate.
- Isocitrate loses carbon dioxide to form α-ketoglutarate.
- α-Ketoglutarate is converted to succinylated CoA.
- Succinylated CoA is converted to succinic acid.
- Succinic acid is converted to fumaric acid.
- Fumaric acid is converted back to fumarate with the help of fumarate enzymes.
These reactions demonstrate how fumarate metabolism is linked to energy. Each step helps cells utilize nutrients and maintain normal metabolic function.
Role in Cellular Energy
Fumarate metabolism contributes to energy production. Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The table below explains this process:
| Enzyme | Process |
|---|---|
| Succinate Dehydrogenase | Succinate loses electrons to FAD, forming fumarate and FADH₂. |
Then, fumarate is converted to malate. This step is crucial for metabolism because it helps cells generate ATP (the primary energy source). Fumarate metabolism also produces building blocks for other molecules. Cells need these building blocks to grow and repair themselves.
Cells need healthy metabolism to remain strong and active. Fumarate metabolism helps maintain high energy levels, allowing the body to function properly.
Those who understand metabolism understand the importance of fumarate. It maintains the normal functioning of the body’s energy system, helping people maintain daily life.
Industrial Production of Fumaric Acid

Fermentation and Biosynthesis
Factory production primarily uses fermentation and biosynthesis to produce fumarate. They utilize specific fungi, such as *Rhizopus nigricans* and *Rhizopus arrhizus*. These fungi can convert plant sugars into fumaric acid. Scientists discovered this ability in *Rhizopus nigricans* in 1911. By 1938, experts found that *Rhizopus* fungi were the most effective. In 1943, some companies began using a new method called deep aerobic fermentation. This method helped them produce more fumaric acid. Today, approximately 85% of fumaric acid comes from fermentation.
The biosynthetic pathway of these fungi is efficient and environmentally friendly. It uses plant feedstocks instead of fossil fuels, which helps protect the environment and supports green development goals. Many companies now use microbial biosynthesis technology. This method is less polluting and more energy-efficient. The process is as follows:
- Workers provide plant sugars to the fungi.
- The fungi convert the sugars into fumaric acid.
- The plant collects and purifies the fumaric acid for use in the food, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors.
Fermentation and biosynthesis are green methods for producing fumaric acid. This helps meet the demand for safe and environmentally friendly products.
In recent years, more and more people have favored biosynthesis. High oil prices and concerns about pollution have prompted companies to choose fermentation. This method not only offers high yields but also complies with strict regulations.
Chemical Synthesis Methods
Chemical synthesis is another method for producing fumaric acid. This method uses petroleum-derived maleic anhydride as a raw material. Workers mix maleic anhydride with water to produce maleic acid. This is then heated to 100°C to 250°C. A catalyst helps convert maleic acid into fumaric acid. This step, called isomerization, yields over 80%. Factories have been using chemical synthesis since the 1940s.
Chemical synthesis is used when factories need to rapidly produce large quantities of fumaric acid. This method can produce fumaric acid with high yields and high purity. The steps are as follows:
- Convert maleic anhydride into maleic acid.
- Heat and add a catalyst to produce fumaric acid.
- Purify the product according to industry standards.
The following table lists the quality standards for industrial-grade fumaric acid:
| Quality Standard | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity for Pharma-grade | ≥99.5% |
| Purity for Food & Industrial | ≥99.0% |
| Heavy metals | ≤10 ppm |
| Microbial limits | Within pharmacopeial requirements |
| Loss on drying | ≤0.3% |
| Compliance | USP, EP, CP standards |
Factory manufacturers must comply with these regulations to use fumaric acid in the food and pharmaceutical industries. High purity ensures personnel safety and guarantees good product performance.
Note: Manufacturing fumaric acid is not easy. Low conversion rates, numerous byproducts, and pH variations increase purification difficulty and costs. New technologies such as chromatography help address these issues and ensure high-quality fumaric acid.
The factory uses both biosynthetic and chemical synthesis methods to produce fumaric acid. Both methods are crucial for meeting global demand. The company places great emphasis on purity, safety, and environmental protection in the production of fumaric acid.
Uses of Fumaric Acid
Food and Beverage Applications
Fumaric acid plays a vital role in food production. Companies add fumaric acid to food products to improve taste and extend shelf life. It helps keep beef and baked goods fresh for longer. Fumaric acid helps control the acidity of beverages such as juice, beer, and cider, enhancing flavor and making food more delicious. Fumaric acid also inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria, thus improving food safety. Regulations governing the use of fumaric acid exist in various countries to ensure public safety.
Fumaric acid helps baked goods retain their acidity for longer and keeps them fluffy and fresh.
Animal Nutrition
Farmers use fumaric acid to help animals grow and maintain health. Fumaric acid helps animals utilize feed better, obtaining more protein. Animals such as pigs, chickens, and fish grow better after adding fumaric acid to their feed. Nile tilapia grow faster and have healthier stomachs with the help of fumaric acid. Fumaric acid also reduces harmful bacteria in the animal’s intestines. This helps animals absorb more nutrients. The table below shows the required amount of fumaric acid for different animals:
| Animal Type | Dosage (kg per ton of feed) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Suckling pigs (7-12kg) | 1 – 1.5 | High acidifier requirement |
| Piglets (12-25kg) | 0.8 – 1 | Adjusted for growth stage |
| Piglets (25-50kg) | 0.5 – 0.8 | Based on physiological state |
| Medium/Large pigs (50kg to market) | 0.3 – 0.5 | For optimal growth performance |
| Pregnant/Lactating sows | 0.5 – 1 | Supports health during gestation/lactation |
| Broilers | 2000 mg/kg (0.2%) | Increases feed intake and digestibility |
Fumaric acid helps animals maintain strength and health. Today, fumaric acid is ideal for farms.
Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care
Fumaric acid is widely used in pharmaceuticals and skincare. Doctors use fumaric acid to treat psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Many psoriasis patients experience significant improvement after using fumaric acid for four months. Fumarate esters, such as dimethyl fumarate, help fight cancer and reduce nerve swelling. These chemicals help protect cells and improve the effectiveness of cancer treatments. Fumaric acid is also found in shampoos and conditioners. It helps balance pH levels, leaving hair feeling smoother. Fumaric acid ensures the safety of bath products by inhibiting bacteria.
Industrial Applications
Fumaric acid has applications in many factories. It helps in the manufacture of resins, coatings, and plastics. These products are used in the construction, automotive, and packaging industries. Fumaric acid makes plastics more flexible. Textile companies use fumaric acid to help dyes adhere better to fabrics. The table below lists the applications of fumaric acid in various industries:
| Application Area | Main Products/Uses |
|---|---|
| Resins | Unsaturated polyester resins, coatings, plastics |
| Pharmaceuticals | Drugs for treating psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, and cancer |
| Processed Foods | Food additives, acidity regulators, preservatives |
| Animal Feed | Acidifiers, improving digestion and absorption |
| Cosmetics | Skincare products with antioxidant properties |
| Detergents and Cleaners | Cleaning Products |
| Polymers and Resins | Alkyd resins, plasticizers |
| Paints and Coatings | Durable coatings for buildings and cars |
| Textile Industry | Dyeing processes |
Fumaric acid helps scientists research cancer and tumors. It has applications in the pharmaceutical, industrial, and food sectors.
Fumaric acid is an important contributor to food safety, animal health, cancer treatment, and new product development.
Fumaric acid originates from nature, the human body, and factories. It is found in fruits and vegetables and helps cells produce energy. Factories also use fumaric acid in food, pharmaceuticals, and other products.
Fumaric acid is widely distributed in nature. It participates in many physiological processes in humans, animals, and plants. In factories, it is initially produced from petroleum and other fossil fuels. The FUMBIO research project will study the amount of carbon dioxide produced when fumaric acid is produced using biotechnology and compare it to the production of fumaric acid from petroleum. Collaborators believe that using carbon dioxide as a feedstock can reduce the carbon footprint and may even achieve negative carbon emissions.
- Fumaric acid is present in many fruits and vegetables and helps the human body produce energy.
- Fumaric acid is used in food to improve flavor and keep food fresh. Approximately 38% of fumaric acid is used in food and beverages.
- Doctors use fumaric acid to treat skin conditions such as psoriasis. This demonstrates its medical significance.
- Detecting fumaric acid levels can help identify health problems, such as genetic or metabolic issues.
Every year, people are exploring new uses for fumaric acid. The world craves safer, more environmentally friendly options. Using products containing fumaric acid is beneficial to both the planet and our health.
FAQ
Which foods are rich in fumaric acid?
Apples, grapes, tomatoes, and carrots are rich in fumaric acid. Boletus mushrooms and white mushrooms are also high in it. Eating these foods provides people with natural fumaric acid.
Is fumaric acid safe to eat?
Fumaric acid is subject to strict food safety regulations. Food agencies state that fumaric acid is safe to use as a food additive. People can trust the safety and quality of foods containing fumaric acid.
How is fumaric acid used in animal feed?
Farmers add fumaric acid to animal feed to aid digestion and growth. Animals are able to absorb nutrients better and remain healthy. Fumaric acid can also reduce harmful bacteria in the gut.
Can fumaric acid treat diseases?
Doctors use fumaric acid as an adjunct treatment for psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Fumarate esters can reduce swelling and protect cells. These effects have led to the widespread use of fumaric acid in modern medicine.
Why does industry favor fumaric acid?
Industry chooses fumaric acid because of its purity, stability, and versatility. It can enhance the strength of resins, plastics, and coatings. Fumaric acid can also extend the lifespan of products and improve their performance.
| Industry Use | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Taste, keeps food fresh |
| Pharmaceuticals | Stays strong, works well |
| Manufacturing | Makes things tough |




