
Fumaric acid is an effective food preservative. It controls the acidity of food and helps it stay fresh for longer. Food manufacturers add fumaric acid to dairy products such as chocolate milk and also use it in cheese and sausage casings. This is because fumaric acid has a very acidic taste, which helps maintain the stability of food. Fumaric acid is also used in pharmaceuticals, animal feed, and other materials. Fumaric acid is generally considered safe. More and more companies are looking for natural food preservation methods, so they are using fumaric acid more frequently.
Key Takeaways
- Fumaric acid is a powerful preservative that helps keep food fresh and inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria.
- It works best in dry foods and can be used in combination with other preservatives to further improve food safety.
- Food manufacturers use fumaric acid in many products, including baked goods, beverages, and confectionery. It helps extend the shelf life of food.
- Experts say that fumaric acid is safe to consume. Health organizations have not set strict daily intake limits for it.
- Fumaric acid helps preserve food naturally without altering its taste or texture.
Fumaric acid in food preservation
How fumaric acid works
Fumaric acid is a powerful preservative that inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria in food. Its acidic components lower the pH of food, thereby inhibiting the survival of bacteria, mold, and yeast. Food can thus remain safe and fresh for longer. Scientists have found that fumaric acid can significantly reduce the number of E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus, especially effective in foods such as lettuce and cabbage.
- Fumaric acid fights many germs:
- It can reduce the number of E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus in vegetables.
- It is also effective against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Fumaric acid is more effective against bacteria than yeast.
| Microorganism | MIC (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Candida tropicalis | 9.375 |
| Candida krusei | 37.5 |
| Candida albicans | 4.687 |
| Candida glabrata | 4.687 |
| Candida parapsilosis | 1.172 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 0.150 |
| Escherichia coli | 0.150 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 0.150 |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 0.150 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0.075 |
Fumaric acid can also inhibit the growth of putrefactive bacteria by destroying bacterial spores. It alters the appearance of spores, preventing their growth. This helps keep food fresh for longer.
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Antibacterial properties | Fumaric acid stops Bacillus cereus spores from growing. |
| Effects on spore structure | Fumaric acid changes spores so they cannot grow. |
| Germination processes | The acid messes up how spores grow. |
Fumaric acid works best in dry foods. It can be mixed with other preservatives to improve food safety. Due to its slow dissolution, it can maintain its effect for a long time. This helps protect food during storage.
Fumaric acid can also regulate the acidity of food. By increasing the acidity of food, it can inhibit the growth of spoilage bacteria. This helps extend the shelf life of food.
Note: Fumaric acid is chosen because it maintains food safety without altering the taste or texture of the food.
Common food uses
Fumaric acid is widely used in a variety of foods. Food manufacturers add it to baked goods, beverages, and confectionery to maintain freshness. It is suitable for moist foods such as tortillas and jams. It helps inhibit the growth of mold and bacteria.
| Food Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Beverages | Soft drinks, juices |
| Baked Goods | Bread, pastries |
| Gelatin Desserts | Jell-O, pudding |
| Confections | Candy, chocolates |
| Dry Mixes | Cake mixes, seasoning mixes |
| Jelly | Fruit preserves |
| Salt Substitutes | Low-sodium products |
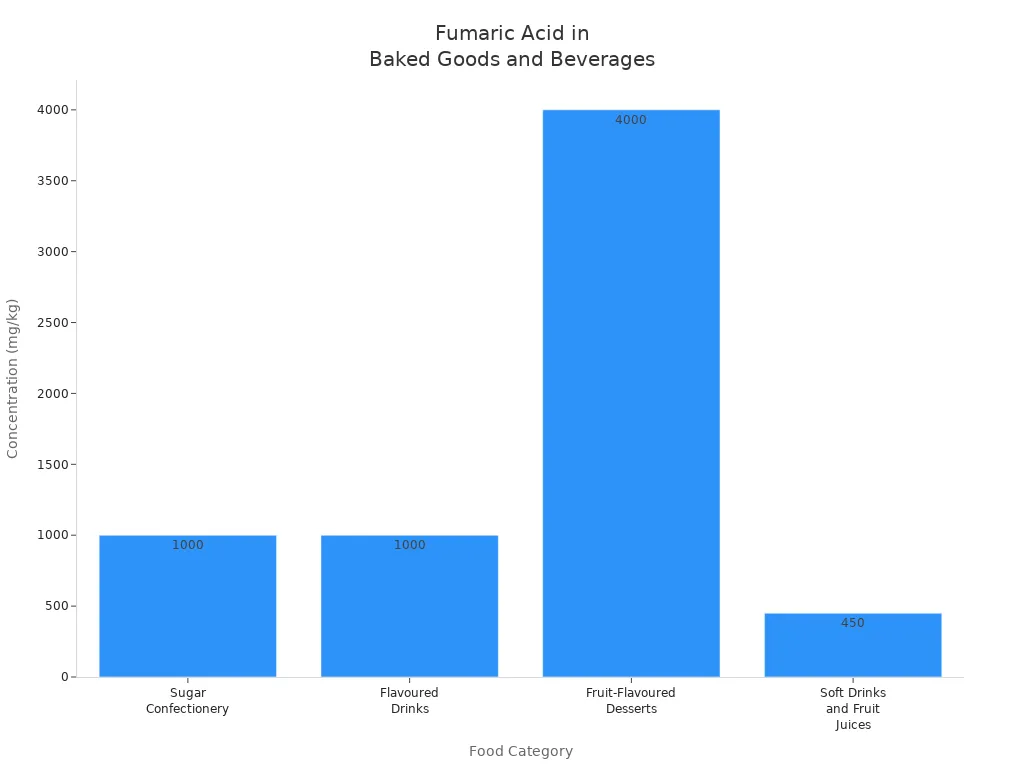
Bread: 0.8 to 1.2 grams of fumaric acid per kilogram. The maximum permissible amount is 3 grams per kilogram. Soft drinks and juices: 300 to 600 milligrams per kilogram. Confectionery and flavored beverages: approximately 1000 milligrams per kilogram.
Fumaric acid has a wide range of uses:
- It keeps bread and pastries fresh.
- It imparts a lasting tartness to candies and beverages.
- It helps jams stay firm and fresh.
- It prevents dry powder mixtures from clumping.
- It keeps dairy products such as chocolate milk smooth.
Fumaric acid is favored for its long shelf life. Its low water absorption makes it ideal for dry powder mixtures and ready-to-eat foods. Many companies use fumaric acid in tortillas, fruit juices, and snacks. More and more people are looking for safe and natural ways to preserve food.
NORBIDAR provides high-quality fumaric acid to food manufacturers to meet these needs. With its expertise and technology, the company is able to obtain reliable food preservation ingredients.
Fumaric acid Effectiveness and comparison
Mold and microbial control
Fumaric acid helps ensure food safety. It inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria. It has good bactericidal effects against bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Scientists have discovered that adding fumaric acid to cider can significantly reduce the number of E. coli. The number of bacteria in broccoli sprouts treated with fumaric acid also decreased. This acid can reduce the number of harmful bacteria in many foods.
Fumaric acid targets certain spoilage microorganisms. It can inhibit the growth of lactic acid bacteria (such as *Lactobacillus plantarum*) in cucumber juice. It can also inhibit the growth of certain molds. In bread, dimethyl fumarate can keep it mold-free for 23 days, while calcium propionate can only keep it mold-free for 12 days.
| Preservative Type | Amount Used (g/kg flour) | Mold-Free Duration (days) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimethyl Fumarate (DMF) | 0.16 | 23 |
| Calcium Propionate | 1.28 | 12 |
Fumaric acid helps extend the shelf life of food. It can prevent food from being attacked by bacteria and mold.
Fumaric acid vs. other preservatives
Fumaric acid differs from other preservatives. It extends the shelf life of food by inhibiting spoilage and controlling pH. Citric acid also extends the shelf life of food by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, mold, and yeast. Both acids help keep food fresh, but their mechanisms of action differ.
| Acid | Shelf Life Extension Capability |
|---|---|
| Fumaric Acid | Improves shelf life by stopping spoilage and controlling pH levels. |
| Citric Acid | Slows down bacteria, mold, and yeast growth, extending shelf life. |
Fumaric acid has more advantages. It is cheaper than citric acid. Because it is heat-resistant, it is ideal for baked goods. It is naturally derived and readily decomposes in the natural environment.
| Aspect | Fumaric Acid | Citric Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Cost-effectiveness | More cost-effective | Generally more expensive |
| Thermal Stability | High | Lower |
| Shelf Life | Long | Varies |
| Solubility | Low | High |
| Onset of Sourness | Slower | Quick |
| Clean-label | Natural origin perception | Commonly used |
Note: Fumaric acid is ideal for food manufacturers. It is safe, has a long shelf life, and is natural.
Fumaric acid Safety and regulations

Food and feed safety
Experts say fumaric acid is safe for both humans and animals. It is safe to use in normal amounts. Many food safety agencies have tested this ingredient and found that adding it to food or animal feed does not cause health problems. The table below lists the safety assessments of major agencies:
| Authority | Statement |
|---|---|
| FDA | Fumaric acid is safe for food and approved for people. |
| EFSA | Fumaric acid is safe for food and animal feed. There is no strict daily limit. |
| Research | Eating normal amounts of fumaric acid does not cause health risks. |
NORBIDAR uses special technology to produce high-purity fumaric acid, with a purity of 99% or higher. High purity means its safety and good performance in food applications. The table below explains the importance of purity:
Researchers tested fumaric acid in fish feed. During the study, they found no harm to the growth or health of the fish.
In a study by Das Neves et al. (2022), juvenile Nile tilapia were fed food containing different concentrations of fumaric acid for 35 consecutive days. The study examined the growth and gut health of the juveniles. The results showed that fumaric acid had no adverse effects on the growth of the juveniles. However, this study did not test for excessive intake, and the duration was not long enough. Therefore, there is currently insufficient information to determine whether fumaric acid is safe for all fish.
Regulatory approvals
Many countries allow food manufacturers to use fumaric acid. Authorities have assessed its safety and determined that it can be used as a preservative. The table below lists these agencies:
| Authority | Determination |
|---|---|
| FDA | Safe for food use |
| EFSA | Safe for food use |
| JECFA | Safe for food use |
NORBIDAR has been producing high-quality fumaric acid for over 15 years. Its products comply with strict regulations.
Side effects and concerns
Most people do not experience problems after consuming food containing fumaric acid. Some people may experience mild side effects if they ingest too much, such as:
- Stomach upset
- Skin redness
- Some people may have poor tolerance to it.
In rare cases, some people may experience:
- Decreased lymphocyte count
- Decreased white blood cell count
- Elevated eosinophil count
- Transient increase in urine protein
- Moderate increase in liver enzymes and bilirubin
Note: These side effects are rare and usually only occur with excessive intake.
Fumaric acid ensures food safety by inhibiting harmful bacteria and molds. Studies have shown that it is more effective than lactic acid in killing bacteria such as Listeria and Escherichia coli. Food manufacturers use fumaric acid to help keep food fresh and stable. Safety agencies in many countries consider fumaric acid safe for use in food and animal feed. The following table lists the opinions of these agencies:
| Regulatory Body | Findings |
|---|---|
| FDA (U.S.) | GRAS for food, with no limit because it is found in the body. |
| JECFA | Set ADI as ‘not specified’, so it is safe even at high amounts. |
| EU | Approved as a food additive (E297) and for medicine. |
Fumaric acid is a reliable and effective ingredient for ensuring food and feed safety.
FAQ
What are the uses of fumaric acid in food?
Fumaric acid can preserve food, impart a sour taste, and help inhibit bacterial growth. Food manufacturers use it in bread, beverages, candies, and sauces.
Is fumaric acid safe to eat?
Experts say fumaric acid is safe for humans. Food safety agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have approved its use in food and animal feed.
Does fumaric acid change the taste of food?
Fumaric acid imparts a sour taste to food but does not mask other flavors. Many people enjoy the sour taste it gives to candies and beverages.
Can people allergic to fumaric acid eat foods containing fumaric acid?
Most people can eat foods containing fumaric acid. Allergic reactions are very rare. People with specific health needs should consult a doctor.
What is the difference between fumaric acid and citric acid?
| Feature | Fumaric Acid | Citric Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Sourness | Strong | Mild |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Shelf Life Help | High | Medium |
Fumaric acid is more resistant to storage and less expensive than citric acid.




